The voice of the people
Kuwait is a fully independent Arab state with a democratic style of government in which sovereignty remains with the nation, which is the source of power. As prescribed by the Constitution, the system of government is based on a separation of powers, although cooperation is also required by the Constitution. Legislative power is vested in His Highness Emir and the National Assembly, while executive power is vested exclusively in His Highness Emir and his Cabinet. Judicial power is vested in the courts acting on behalf of His Highness the Emir within the framework established by the Constitution.Constitution
The State of Kuwait has a written Constitution defining Kuwait as a hereditary emirate with inheritance rights limited to the descendants of the late Emir, His Highness Sheikh Mubarak Al-Sabah. It consists of 183 articles, divided into 5 chapters: (a) State and governmentsystem; (b) The main components of Kuwaiti society; (c) Fundamental rights and obligations; (d) Powers; (e) Basic and conditional laws. The constitution of the state of Kuwait is based on democratic principles and combines the positive aspects of both the presidential and parliamentary systems that are prevalent in other democratic countries of the world. One of its fundamental conditions is that sovereignty and power belong to the people. The basic principles of the Constitution are the sovereignty of the state, public freedom, and equality before the law. The constitution was drafted by
the Legislative Assembly, consisting of 20 elected members. The late Emir of Kuwait, His Highness Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salem Al-Sabah, ratified Constitution 14 of Jumad II 1382 or November 11, 1962. It entered into force on January 29, 1963. The Constitution provides for a National Assembly (Parliament), which consists of 50 members directly selected by universal suffrage and secret ballot (Article 80) in accordance with the law. The meeting is elected for four years. Part III of the Constitution guarantees human rights and freedoms, such as freedom from accidental arrest, freedom of the press, freedom of communication and the right to secret assembly. Some of these constitutional guarantees are subject to legal regulation.
The Crown Prince
Kuwait The current Crown Prince of Kuwait, His Highness Sheikh Saad Al-Abdullah Al-Salem Al-Sabah, was appointed Crown Prince on January 31, 1978, and as Prime Ministeron February 8, 1978. In these dual positions, Sheikh Saad is
President of the Supreme Defense Council, Supreme Petroleum
Council, Civil Service Commission, and the Higher Housing Council.
He is the eldest son of the last Emir of Kuwait, His Highness Sheikh
Abdullah Al-Salem Al-Sabah. Article 4 of the Constitution stipulates the condition for the appointment of the Crown Prince: "The throne will be appointed, at the latest, one year after the accession to the throne of Emir."
Council of Ministers
Executive power is vested in the Council of Ministers. ThePrime Minister, according to tradition, is the Crown Prince
appointed by the Decree of the Emir.
Emir of Kuwait
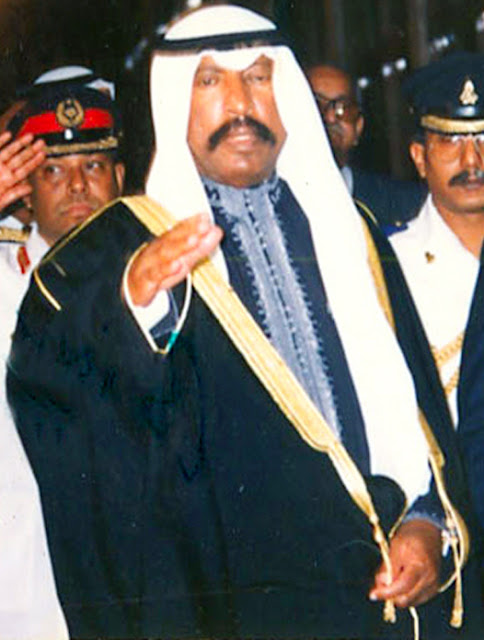
"The emir is the head of state. His personality is protected and inviolable." The constitution states that Emir takes to power through his ministers. The Prime Minister and ministers arecollectively responsible to the Emir for the general policy of the state, and each minister is responsible for his ministry. The emir is also the supreme commander of the armed forces. Kuwait is a hereditary emirate whose succession is passed on to the descendants of His Highness Mubarak Al-Sabah. The executive power belongs to Emir, the head of state, who is elected by members of the ruling family from this family. Emir appoints the Prime Minister and other ministers on the recommendation of the Prime Minister. There are 16 ministers in the Cabinet. The current Emir, His Highness Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, born in 1928, rules since 1978.
National flag |
National emblem
The coat of arms of Kuwait consisted of a “helmet with a falcon
and two intersecting flags above them”, this was until mid-1963
when the Council of Ministers decided to replace it with a new
one. Kuwait's current coat of arms is a falcon with outstretched
wings spanning a single-masted Arab ship sailing in white and
blue waves. It is a symbol of the Kuwaiti maritime tradition.
and two intersecting flags above them”, this was until mid-1963
when the Council of Ministers decided to replace it with a new
one. Kuwait's current coat of arms is a falcon with outstretched
wings spanning a single-masted Arab ship sailing in white and
blue waves. It is a symbol of the Kuwaiti maritime tradition.
National Anthem











.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment
Please Dont Enter Any Spam Link in The Comment Box